Abstract
PURPOSE Technology could transform routine decision making by anticipating patients’ information needs, assessing where patients are with decisions and preferences, personalizing educational experiences, facilitating patient-clinician information exchange, and supporting follow-up. This study evaluated whether patients and clinicians will use such a decision module and its impact on care, using 3 cancer screening decisions as test cases.
METHODS Twelve practices with 55,453 patients using a patient portal participated in this prospective observational cohort study. Participation was open to patients who might face a cancer screening decision: women aged 40 to 49 who had not had a mammogram in 2 years, men aged 55 to 69 who had not had a prostate-specific antigen test in 2 years, and adults aged 50 to 74 overdue for colorectal cancer screening. Data sources included module responses, electronic health record data, and a postencounter survey.
RESULTS In 1 year, one-fifth of the portal users (11,458 patients) faced a potential cancer screening decision. Among these patients, 20.6% started and 7.9% completed the decision module. Fully 47.2% of module completers shared responses with their clinician. After their next office visit, 57.8% of those surveyed thought their clinician had seen their responses, and many reported the module made their appointment more productive (40.7%), helped engage them in the decision (47.7%), broadened their knowledge (48.1%), and improved communication (37.5%).
CONCLUSIONS Many patients face decisions that can be anticipated and proactively facilitated through technology. Although use of technology has the potential to make visits more efficient and effective, cultural, workflow, and technical changes are needed before it could be widely disseminated.
- health information technology
- screening
- decision making
- computer-assisted
- patient education
- primary care
- practice-based research
INTRODUCTION
Today’s patients face complex medical decisions. Clinicians traditionally support patients with decisions by giving advice during in-person visits. Unfortunately, the competing demands and time constraints associated with office visits limit the help clinicians can realistically provide.1,2 More importantly, both difficult and even routine choices might entail a “decision journey”—that is, the support required may extend over time, a period during which patients may contemplate options, gather additional information, confer with family and friends, consider personal preferences, and address worries or concerns.3–5 These tasks are beyond what can be accomplished during an office visit.6–9
Although the components of a “good” medical decision journey have been well described,10–13 patients generally receive limited support during these journeys.14–17 Patients want to be included in decisions, yet many decisions occur with minimal patient input.17–19 When conversations do take place, they rarely include all elements needed for an informed decision.14,18,20 One proven solution is to use decision aids. Decision aids increase knowledge, reduce decisional conflict, engage patients, and reduce rates of elective invasive procedures and unnecessary testing.21–23 Yet it is difficult for clinicians to routinely use decision aids, and accordingly, they are not commonly used.24–29
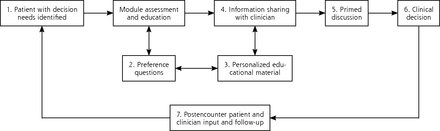
Health information technology (HIT) offers a potential to systematically automate decision-making processes outside the constraints of clinical encounters. This strategy could enable visits with clinicians to focus on decision elements that occur best in person.30,31 HIT has the capacity to anticipate decision needs through programmed logic, deliver information and decision support before visits, collect patient-reported information, share information with the clinician about where the patient is with decisions and preferences, set a decision-making agenda, and even follow up on next steps (Figure 1).
Conceptual model for engaging patients through an informed decision-making module embedded in a patient portal and electronic health record.
Note: To engage patients in their decision, the informed decision-making (IDM) module guides patients and clinicians through a series of 7 steps that can be applied to a wide range of decisions beyond the test case (cancer screening) investigated in this study. The IDM module (1) reaches patients outside the confines of an office visit to explore a potential decision by completing the module; (2) walks patients through an intake that assesses personal preferences, knowledge, and needs, and patients’ readiness to make a decision; (3) provides personalized educational material tailored to patients’ stated preferences and decision stage; (4) allows patients to share their preferences and decision needs with their clinician; (5) prompts patients and clinicians to use the reported information to make a decision; (6) guides the patient to make a choice, which can include deferring the decision; and (7) invites patients and clinicians to provide input after the encounter.
METHODS
This pragmatic observational cohort study evaluated how clinicians and patients used an integrated decision module and explored the module’s impact on care for 3 routine decision scenarios: when to start breast cancer screening, how to be screened for colorectal cancer, and not being screened for prostate cancer. These 3 screening topics were selected because they represent common patient decisions—even prostate cancer screening, which although not recommended for the general population, is often inquired about by patients and may be appropriate for a subset of men willing to risk screening harms.32 The study was reviewed by the Virginia Commonwealth University Institutional Review Board (HM14750).
Setting
Twelve primary care practices in northern Virginia participated. The practices shared 1 of 2 electronic health records (EHRs), Allscripts Enterprise or Professional. All practices used a central patient portal, called MyPreventiveCare.33 At the time of the study, 55,453 unique patients (34.5% of the practice population) had a portal account and 23,546 used the portal during the study period. Although portal users were representative of the practices, prior investigation demonstrated users were more likely to be older or have comorbidities, and were slightly less likely to be African American or Hispanic.34
Participants
Patients age 50 to 75 years who were overdue for colorectal cancer screening,35 women aged 40 to 49 years who had not had a mammogram in 2 years, and men aged 55 to 69 years who had not obtained a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test in 2 years were invited to complete the decision module. Patients were excluded if they had a prior diagnosis of colorectal, breast, or prostate cancer, or prior abnormal screening test results.
Invitations to use the module occurred in 3 phases. In phase 1 (January 6, 2014, through February 16, 2014), eligible patients who logged into the portal were prompted to review the module. In phase 2 (February 17, 2014, through May 15, 2014), eligible patients who had a visit scheduled 2 weeks in advance were e-mailed an invitation to review the module, 2 weeks, 1 week, and 2 days before their visit. In phase 3 (May 26, 2014, through August 15, 2014), any eligible patient was e-mailed up to 3 weekly invitations to review the module, irrespective of appointment status.
Decision Module
The decision module promoted the 2012 prostate, 2009 breast, and 2008 colon cancer screening recommendations made by the US Preventive Services Task Force.32,35,36 It included 7 components (Figure 1). The system identified eligible patients through well-established programmed logic by querying the EHR and portal data.33 It flagged eligible patients when they used the portal (phase 1) or during a daily scheduled query (phases 2 and 3) and then invited patients by prompt or e-mail to complete a previsit assessment in the decision module. Seventeen interactive questions explored patients’ stage of readiness for deciding about cancer screening, information needs and fears, desired assistance, preferred format for receiving information and statistics, and planned next steps.
Based on patients’ responses, the module assembled a customized educational page that included information about topics of greatest interest to patients (eg, risk of cancer, benefits or harms of screening, screening logistics) in the format they preferred (ie, words, numbers, pictures, or stories). Questions were derived from validated instruments when possible.37–39
The module asked patients if they would like to discuss screening at their next office visit and if they would like a summary to be automatically forwarded to their clinician for review. The summary included whether patients had made a screening decision, the topics they wanted to discuss, their fears and worries, and their preferred level of decision control.37 Supplemental Appendix 1, available at http://www.annfammed.org/content/15/3/217/suppl/DC1/, displays screenshots of MyQuestions, educational content, and clinician summaries. The system automatically sent a postencounter questionnaire to both the patient and clinician after the office visit. The questionnaire sought feedback on the module and the events before, during, and after the clinical encounter. Nonresponders received up to 5 reminders.
The design of the module was informed by a 2-year process of patient and stakeholder engagement including focus groups to identify important module content; patient iterative input of draft module content; cognitive and usability testing consistent with national standards40; and a patient, clinician, and health system workgroup that met quarterly for 2 years to help plan the decision module design, implementation, and interpretation of findings.41 A clinician from each practice served on the clinician workgroup and helped to standardize and promote implementation at his or her office.
Outcomes
Primary outcomes included measures of how the decision module was used and its impact on decision making. We used 5 data sources: (1) the EHR (demographics, diagnoses, screening status, module eligibility), (2) the portal (health risk assessment responses, prompt, or e-mail invitation receipt), (3) the decision module (patients’ responses, paradata–clicks within the decision module pertaining to use of educational materials),42,43 and (4) the patient postencounter questionnaire and (5) the clinician postencounter questionnaire (see Supplemental Appendices 2 and 3, respectively, for the questionnaires, available at http://www.annfammed.org/content/15/3/217/suppl/DC1/).
Decision module uptake—measured by the number of eligible patients who started and completed the module—was calculated by race, ethnicity, sex, preferred language, insurance type, and phase of module invitation. Measures of module use included educational content patients reviewed (paradata), whether patients elected to share responses with their clinician, and whether patients believed their clinician reviewed their forwarded summary. EHR data indicated whether patients obtained breast, colorectal, or prostate screening within 3 months of using the module.
Analysis
The analysis included all patients with a MyPreventiveCare account who met eligibility criteria. Patients were subdivided into starters and nonstarters, and starters were further subdivided into completers or noncompleters. We used χ2 tests for independent group comparisons, generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs) for dependent group comparisons, and ANOVA to compare time to follow-up between groups. We used a GLMM when comparing phase eligibility to include a patient-level random effect that accounted for patients being eligible in multiple phases. We did not adjust for other covariates. All analyses were completed using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute).
RESULTS
Decision Module Use
During the nearly 1-year study period, 11,458 patients (20.7% of 55,453 unique portal users) faced a screening decision for colorectal cancer (6,329 patients), breast cancer (3,733 patients), or prostate cancer (1,396 patients) (Table 1). Prompted by the invitation, 2,355 patients started and 903 completed the module. Patients faced with a prostate cancer screening decision were most likely, while patients faced with breast cancer screening were least likely, to start and complete the module (P <.001).
Patients Starting and Completing the Informed Decision-Making Module by Study Phase and Cancer Screening Decision
Patients eligible in phase 2 were most likely to start the module (phase 1, 2, and 3 = 20.6%, 30.7%, and 9.8%, P <.001) and complete the module (phase 1, 2, and 3 = 7.9%, 21.1%, and 3.6%, P <.001) (Table 1). Although phase 3 had the lowest percentage of starters and completers, because many patients were included in phase 3, it yielded the largest absolute number of starters and completers. A detailed analysis of module attrition has been previously reported.44
When the module was used, paradata indicated that 291 patients (23.6%) clicked on at least 1 educational resource in the module (Supplemental Appendix 1, section 16)—an average of 3.5 resources per patient. The most frequent information patients reviewed were options for getting screened (206 patients, 70.8%), what screening test works best (145 patients, 49.8%), problems or complications from screening (133 patients, 45.7%), and how the test is performed (120 patients, 41.2%). Among the 1,044 patients who reached the forwarding question, 493 (47.2%) indicated a desire to forward a summary to their clinician.
Characteristics of Decision Module Users
Women were less likely than men to use the module (Table 2). Within the colorectal cancer screening cohort, which included both sexes, more men started the module (P =.03). Similarly, across all phases, men were more likely than women to share a summary with their clinician (56.3% vs 37.0%, P <.001). Module use was lower for patients with no prior screening than for those previously screened (P <.001) and for patients who preferred a language other than English (P <.001). Hispanics tended to be less likely than non-Hispanics to start the module (P =.07). Factors other than socioeconomic status also appeared important. Asian patients, a demographic with often high socioeconomic status,45 were least likely to start the module (P <.001), and African American patients were most likely to complete it (P <.001). Start and completion rates were higher for Medicare beneficiaries than for commercially insured patients (P <.001).
Use of the Informed Decision-Making Module by Demographic Characteristics
Impact on Care
The next office visit occurred, on average, 50 days (range, 0–312 days) after the decision module session. The average differed by phase (phase 1 = 160 days, phase 2 = 7 days, and phase 3 = 14 days; P <.001), although some patients in each phase did not have a visit after module use. About 50% to 60% of patients and clinicians reported the clinician reviewed the forwarded summary before the visit. Patients reported that screening was discussed more often during wellness visits than during chronic or acute care visits (82.5%, 63.9%, 60.0%, respectively, P =.03) (Table 3). Patients who forwarded a summary were slightly more likely to report discussion of screening than those who did not (72.9% vs 67.7%, P =.04).
Satisfaction With the Informed Decision-Making Module and Reported Impact on Care
A sizable subset of patients and clinicians (30% to 50%) reported that the module prompted cancer screening discussions, helped patients get more involved, improved knowledge, enhanced communication, made clinicians more sensitive to patients’ concerns, and facilitated decisions (Table 3). Although only 39.0% of clinicians recalled addressing the patient’s fears/worries, 80.9% of patients said the clinician helped reduce their fears/worries.
Module completion was associated with screening behavior (Figure 2): completers were more likely to get screened within 3 months than nonstarters and noncompleters (P <.001), a pattern suggesting that they had already made a screening choice—mostly to get screened. Among patients eligible for colon cancer screening, completers were more likely than nonstarters to get a colonoscopy (P <.001) or a stool test (P <.001). Comparing nonstarters with completers, there was a greater increase in colonoscopies than stool tests for the latter (P <.001).
Relationship of the informed decision-making module with follow-up visits and with breast, colorectal, and prostate cancer screening.
PSA = prostate-specific antigen.
Note: Percentages of patients who received screening tests were derived from electronic health record data for a period of 3 months after completion of the decision module. Although the colorectal cancer screening rate appears low, this study included only the subset of practice patients overdue for that screening. On the basis of prior studies and practice quality program participation, about 70% of patients in the study practices have been screened for colorectal cancer.46
DISCUSSION
This pragmatic observational cohort study harnessed EHR data and patient portal capabilities to create an automated decision module that could identify patients likely to be facing common cancer screening decisions, engage and inform patients, clarify questions and fears, identify next decision steps, and improve the decision-making process. We found that practices had large decision burdens—with 1 in 5 patients facing a decision—yet only 20.6% of patients facing a decision started and 7.9% completed our decision module. Users reviewed a range of topics, and one-half of patients forwarded their priorities and concerns to clinicians. Both patients and clinicians reported that module completion helped with decisions: one-third to one-half reported it made appointments more productive, got patients more involved in decisions, broadened knowledge, and improved communication.
Our proposed decision module is appealing, yet a clear challenge is getting patients to use such a system. Decision support use is high in the context of clinical trials.23,25 Routine use of decision support in clinical practice, which we tried to automate in this study, is low (9% to 10% of encounters in implementation trials), however.26 Furthermore, pragmatic trials looking at patient portal use frequently demonstrate low initial uptake with increasing use over time as the portal becomes part of new standard workflows.47,48
Our findings regarding patient use by phase provide some insight into how such systems could be integrated into workflow. Linking invitations to visits (phase 2) resulted in greater response rates and less time between portal use and visits; inviting anyone with a need (phase 3) resulted in a greater absolute number of users and may have prompted needed visits. Findings further suggest some groups of patients (possibly men more than women and African Americans more than Asians) and types of decisions (prostate cancer screening more than breast cancer screening) may derive greater benefit from a decision module, but comparison trials are needed to fully understand these observations.
Most trials of traditional decision aids demonstrate reduced use of services with marginal benefit and increased use of beneficial services.23,49–52 Although Figure 2 shows decision module users had higher rates of breast and prostate cancer screening, which may not be good for screening services with small or zero net benefit, users self-selected, and module responses indicated a substantial proportion were already inclined to be screened. Randomized controlled trials of similar systems and trials that assess whether decisions better align with values are needed. Additionally, longer observational periods are required to see the full increase on desired colorectal cancer screening.
This feasibility study had limitations. It involved a large population but lacked controls. It relied on surveys to gauge associations. Completers were more likely to be screened, but this self-selected sample may have been more motivated than other patients. We conducted paired postencounter surveys to elicit feedback from patients and clinicians after visits; overall response rates were 45%, and the rate of paired responses was lower.
Confirming this study’s findings in controlled trials will be important and has implications well beyond cancer screening. Health systems and payers could expand the role of portals to help patients prepare for other complex decisions. Implementing this model of using technology for decision making is likely to encounter technologic challenges,53–56 and engaging patients online and integrating the process with practice workflow may not be easy. If, however, future research confirms the benefits of this approach—more informed patients, better decisions, and wiser use of encounter time—the return on investment could offset the implementation costs and improve care.
Acknowledgment
Our practice partners at Privia Medical Group and Fairfax Family Practice Centers provided their insights and hard work; they include Broadlands Family Practice, Family Medicine of Clifton/Centreville, Fairfax Family Practice, Herndon Family Medicine, Lorton Stations Family Medicine, Prince William Family Medicine, South Riding Family Medicine, Town Center Family Medicine, and Vienna Family Medicine.
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest: authors report none.
Funding support: Funding and support for this project was provided by the Patient Centered Outcomes Institute (PCORI grant no. IP2PI000516-01) and National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (CTSA grant no. ULTR00058).
Disclaimer: The opinions expressed in this manuscript are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the funders.
Supplementary materials: Available at http://www.AnnFamMed.org/content/15/3/217/suppl/DC1/.
- Received for publication September 18, 2016.
- Revision received December 22, 2016.
- Accepted for publication December 31, 2016.
- © 2017 Annals of Family Medicine, Inc.