Abstract
PURPOSE Although studies have shown that more temporally regular (TR) primary care visits are associated with improved patient outcomes, none have examined what clinic staff can do to encourage greater TR visits. This study aims to increase understanding of factors related to health care staff dynamics that contribute to more TR primary care visits for adults with chronic health conditions.
METHODS We conducted semistructured interviews with 15 primary care physicians, 12 nurses, 15 administrative staff, and 4 pharmacists at 12 clinics; one-half characterized as high-TR clinics where patients had regular follow-ups, and the other as low-TR clinics. Interviews were audiotaped, transcribed, and coded using Atlas qualitative data analysis software (Lumivero, LLC).
RESULTS Themes emerged regarding best ways to promote regular follow-up of patients with chronic conditions. These strategies included having a system to encourage follow-up (beginning with administrative staff reaching out to patients and ending with recruiting the help of patients’ family members), routine staff meetings, adaptive workflow, dealing with bureaucracy on patients’ behalf, informal channels of communication with patients, and consulting social workers. Clinics with more regular follow-up emphasized teamwork, a peaceful approach toward challenging patients, and flat as opposed to hierarchical organizational structures for personal relationships among staff.
CONCLUSIONS Teamwork between staff members in primary care settings can contribute to more proactive care delivery, with greater potential to prevent long-term complications. The findings suggest that a high-functioning multidisciplinary care team that focuses on creating the right sorts of interactions and teamwork among members of the staff can contribute to engaging patients more effectively.
- regular follow-up
- primary care settings
- teamwork
- health care staff dynamics
- patients with chronic conditions
INTRODUCTION
For adult patients with chronic conditions, the advice is often to “see your doctor regularly,” because this is thought to promote a more proactive and therefore a more effective style of health care.1 This advice could be divided into 2 parts—see “your” doctor (as opposed to a different doctor) “regularly” (as opposed to only when you feel sick). Following up with one’s main doctor is called “continuity of care” (COC) and there have been many published studies showing that higher COC is associated with improved patient outcomes.2 Only more recently have there been studies about the impact of seeing the primary care physician (PCP) at more regularly spaced intervals in time, which we have called “temporal regularity” (TR). Unlike visits to address an urgent problem, the purpose of prescheduled primary care visits is to deliver proactive care that is intended to improve outcomes for patients with chronic disease. The interval between scheduled visits is determined by the doctor’s assessment of the patient’s condition and how soon he/she will need to follow up to ensure that chronic conditions can be kept under control. We calculated TR for each patient with at least 1 chronic condition by looking at the intervals between primary care visits during 2 consecutive years for that patient, as we will describe below in the Methods section.
Studies have shown that patients with more temporally regular care (higher TR) have better outcomes than patients with lower TR, after controlling for other factors.3-7 Our group has recently published an analysis showing that the effect of TR on patient-level hospitalizations and mortality is also unchanged after controlling for COC.8
Now that we know that TR is an important contributor to better outcomes for patients with chronic conditions, one of the questions that arises is whether we can encourage higher TR. One way to approach this question is to take advantage of the fact that some clinics already have much higher TR than others, after accounting for patient-level factors.6,9 By learning from what these clinics already do, and by contrasting it with low-TR clinics, we can learn about strategies that are clearly at least somewhat feasible—because they are already being used. This sort of study, which takes advantage of natural variation to learn how to emulate the high-performing clinics, is known as a positive deviance study.10,11 Here, we conducted a positive deviance study to compare clinics within Leumit Services (LHS), a large health maintenance organization in Israel. We visited clinics among the highest and the lowest TR in LHS, after accounting for patient factors.9
Teamwork and collaboration among health care professionals in primary care have been suggested as pivotal for improving health outcomes among patients with chronic conditions.12,13 Literature regarding how health care teams function and the structuration model of collaboration14,15 emphasize the importance of shared goals, acknowledgment of the roles of different professional groups,16,17 shared responsibilities, and encouragement of partnership through open communication.18,19 Additional aspects to consider for how teams function include interdependency, which helps health care workers to make the best use of the expertise of each professional on the team to address patients’ needs, and power relationships among team members, which can be flat or hierarchical.20,21
Although there is some understanding of how these factors contribute to higher-functioning health care teams, no previous study has examined how they may contribute to achieving regular follow-ups for patients with chronic health conditions. We thought it was important to include the perspectives of administrative staff, who are often omitted from studies of health care team dynamics and might be key in contributing to TR.12,16
In Israel, the scope of administrative staff’s work at primary care clinics is to oversee and attend to the needs of the medical staff (eg, physician, nurse, pharmacist, social worker). They mainly perform front-office duties including scheduling appointments for patients and helping to manage the daily workflow at the clinic.
In this study, we aimed to understand the factors that contribute to more temporally regular primary care visits for adults with chronic health conditions.
METHODS
Study Design: Overview
This study is based on a descriptive, exploratory, qualitative research design.22,23 It is part of a larger mixed methods study of TR conducted within LHS. In a previous publication, we showed that LHS clinics had a wide range of average TR, after adjusting for differences in case mix.9 For each patient, we calculated the mean interval between visits (in days), and the SD of that mean. We then divided the SD by mean (ie, a coefficient of variation, or CoV). Further details are available in our previous publications.8,9 In this study, we approached staff at 6 clinics with extremely high TR and 6 clinics with extremely low TR based on our initial TR calculations to request their participation. As is usual for positive deviance studies, we included clinics with both high and low TR. These clinics represented different parts of Israel, and served patient panels of diverse socioeconomic status, 5 of which served primarily patients belonging to the Arab society in Israel. We conducted 46 semistructured interviews with health care professionals, including PCPs, nurses, pharmacists, and administrative staff.
The number of staff employed (clinic size) varied. We focused on staff working full-time in the clinic. While some clinics had as many as 2 PCPs, 2 nurses, 3 administrative staff, and 2 pharmacists, others had 1 of each.
We developed a semistructured interview guide,24,25 informed by a review of the relevant literature,26,27 the Organizational Dimensions of the Structuration Model of Collaboration,28,29 and Sullivan’s framework of collaboration.30 The interview guide included these topics: (1) role and work relationship among staff members, (2) decision about follow-up intervals and discussion with patients, (3) incentives and strategies to encourage regular follow-ups, (4) staff’s perceived responsibility and procedure for follow-ups on patients, (5) experience with patients who do not adhere with recommendations. The interviews lasted between 20-50 minutes (average 30 minutes). We continued to add study sites until we had achieved thematic saturation.31 All interviews were audio recorded. The study was conducted from July 2022 to September 2023 and received ethics approval from the Helsinki Committee of LHS (LEU-0008-22).
Participants
Study participants were part of the health care staff as described in the literature,32 including PCPs, nurses, administrative staff, and pharmacists (Table 1), recruited from LHS clinics at different sites in different parts of Israel. The investigator at LHS (A.G-C.) e-mailed the administrative staff at each clinic to invite participation. Once the contact person (the administrator) at the clinic e-mailed back with an initial agreement to participate in the study, the principal investigator (A.R.) e-mailed him/her to provide more information about the study and to introduce the interviewer (M.K.). Then the interviewer (M.K.) set a date to visit the clinic. There were relatively few staff at even the largest clinics we visited. Therefore, most staff members at each clinic were interviewed. Interviewees provided informed consent to participate and to be recorded. Of the 16 clinics approached, 12 agreed to participate.
Characteristics of Participants of the 12 Clinics
Analysis
Data analysis was performed by 3 researchers: a PhD communication expert (M.K.); a PhD qualitative researcher in public health (L.S.); and A.R. (principal investigator, a mixed methods researcher and primary care physician). We entered transcripts into Atlas qualitative data analysis software (Lumivero, LLC). Data analysis was thematic to compare and contrast responses, identify recurring themes, and organize them into categories.33,34 We analyzed in 3 rounds. First, using an iterative process, the 3 researchers independently coded 5 transcripts to identify codes that are more general, coming together to reconcile coding decisions and develop a codebook. Second, according to the codebook, the 3 researchers coded an additional 4 transcripts to identify purposeful codes and allow for revisions of the codebook (Supplemental Table). The researchers discussed all differences at each stage until agreement was reached. Third, one of the researchers (M.K.) coded the rest of the transcribed interviews and consulted with the others in case of emerging issues with the codes. The themes and categories were refined, organized, and merged through agreement.35
RESULTS
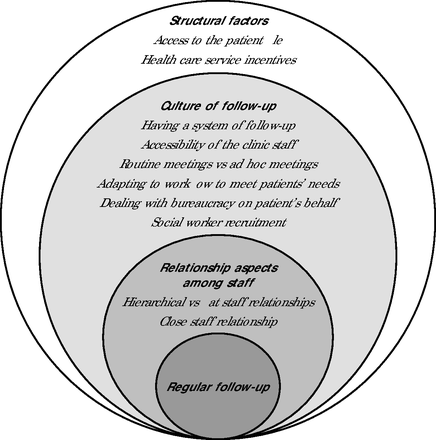
We found 3 main themes that contribute to more regular follow-up of patients with chronic conditions (Figure 1): (1) relationship among staff members, (2) culture of follow-up at the clinic level, (3) structural factors. For each theme there were subthemes, as discussed below.
Main Characteristics of Staff Contributing to More Regular Follow-Up and Continuity of Care of Patients With Chronic Conditions
Relationship Aspects Among Staff Members
The following aspects of relationships among the staff facilitated regular follow-ups at the high-TR clinics and related to close staff relationships and flat staff organization structures. Further, the high-TR clinics were characterized by a peaceful approach toward challenging patients. These relational aspects are summarized in Table 2.
Relationship Aspects Among Staff Members and Between Patients and Staff
Low- and high-TR clinics described the hierarchical relationships among the staff. According to interviewed nurses and administrative staff, the PCP was perceived as the authority figure within the health care team and as an authority figure for patients, further encouraging patients to follow up on recommended treatments. What seemed to characterize the high-TR clinics, however, is that PCPs aligned their role with the nurse and the administrative staff. As shared by the following PCP:
“There are those who think that the doctor is everything. I am part of the system. At this clinic, the staff consists of 4. I am worth less without the nurse, and without the administrator I can’t do it. We complement each other.”
Staff members depended on each other, and often their efforts to support follow-up were complementary. As one administrator at a high-TR clinic suggested:
“Patients might relate more to me, to the nurse, or the doctor. The patient might communicate with the doctor. The doctor will tell me what the patient said if I need to know. Then we convene and process together.”
Whereas, at a low-TR clinic an administrator described how he felt disengaged from the process of follow-up:
“There is a list for patients with performance levels, we [administrative staff] are less involved, it is for the nurse and the doctor.”
Culture of Follow-Up at the Clinic Level
Staff members at high-TR clinics described a clear system to ensure follow-up for “no show” patients. In contrast, low-TR clinics generally did not have a clear system. The system at high-TR clinics generally included the following 6 aspects:
Having a System of Follow-up
At the high-TR clinics, the staff worked hard as a team to reach out to patients who did not follow-up with the PCP’s recommendations. They described a 4-step plan. First, the administrative staff was assigned to prepare the “no show” list and contact patients who did not proceed with the recommended treatments on a fixed interval. Second, the nurse would reach out to patients who did not follow-up after the administrator had contacted them. Third, the PCP contacted those patients who still did not follow-up. Fourth, staff members asked the help of the social worker or a family member to reach out to patients who still did not follow-up. Participants quotes are provided in Table 3.
The 4-Step Model of Follow-Up at the High-TR Clinics
Informal Channels of Communication
Interviewees from all clinics described different ways that patients can communicate with the staff. At the high-TR clinics, however, staff members were more frequently engaged in informal modes of communication with the patient, such as sending a personal WhatsApp (Meta Platforms Inc) message. One administrator told us:
“They [patients] will always have an address to turn to. Even my personal cellphone. I try every day to reply to all the messages, to everyone. So, if they cannot reach the desk secretary, I can respond via WhatsApp.”
In contrast, at low-TR clinics, the staff explained that they cannot be available all times: “I have no problem with giving away my number. I just say that I am not always available.”
Routine vs Ad Hoc Meetings
We found that high-TR clinics scheduled monthly or biweekly all-staff meetings specifically to address issues related to no-show patients. For example:
“We meet monthly, I ask the nurse to print out the no show list and we sit and discuss. Unless there is a situation that cannot wait, in which case we meet before.” (PCP)
“We meet weekly and discuss the patients who did not show or had abnormal blood tests. We discuss what to do.” (PCP)
“We (the staff) decided on a specific day of the week to follow on ‘no show’ patients, and to meet and work on it together.” (Nurse)
In high-TR clinics, interviewees emphasized the importance of staff being present during these meetings, including the administrative staff. At the low-TR clinics, there were no regular meetings to address the issue of no-shows, and staff addressed this issue individually, if at all. For example, one PCP shared: “I notice if a patient did not come, and just make the call [myself].”
None of the 6 low-TR clinics held regular meetings for patient tracking and engagement. As one nurse shared:
“We do not have [such a] system. We mainly remember things, or the doctor will come [see us] between patients to inform us the patient did not arrive. Of course, there are things that we do not remember, and they get lost.”
Adapting Workflow to Meet Patient Needs
High-TR clinics emphasized the strategy of adapting the workflow to help give the most challenging patients every opportunity to follow up with the physician. Referring to challenging patients, one nurse described: “Sometimes the doctor may run late with the appointments. [The patient] may lose his patience. So, I invite [the patient] to my office to measure blood pressure and stuff. This way they will not run away.” Another PCP said: “For these [challenging] patients, I book double appointments.” Staff at low-TR clinics mentioned fewer of these sorts of creative strategies, even when asked explicitly. For example, one PCP said: “I do not try to make anyone do anything, I cannot force them [patients].”
Dealing With Bureaucracy on the Patient’s Behalf
The staff at high-TR clinics stated that they help patients to follow up on recommended treatments by offering to schedule appointments. For example, an administrator said: “I help with scheduling appointments. I send the fax, I make the appointment, so [the patient] will follow through with the treatment.”
Social Worker Recruitment
As part of efforts to improve the follow-ups of patients, the high-TR staff recruited the social workers’ help to understand the circumstances of patients or to address barriers faced by patients (Table 3). Low-TR staff did not mention this strategy.
Structural Factors to Achieve Higher Performance Levels
Participants described 2 main structural factors that had an impact on TR.
Access to the Patient File
When asked about efforts to follow-up with patients, administrative staff from low-TR clinics emphasized that they have limited access to patient files, making it harder for them to initiate follow-ups. One administrator said: “I do not have access to medical files, I cannot tell [which ones are] the chronic patients. So, I cannot initiate follow ups.” Administrators at high-TR clinics found ways to bypass this limited access by screening each patient once they enter the clinic:
“The patient enters the clinic. [At that time], I can see which parameters are missing and I tell the nurse.”
“Recently, the system shows us that a certain patient, for example…must undergo certain tests. So, when we see in the system that the patient has the red square next to his name, we direct him to the nurse.”
Health Care Service Incentives
Staff at the high-TR clinics mentioned incentives, such as a day off for a staff picnic, provided by the LHS administration for clinics that have achieved high performance levels of obtaining needed tests for certain patients. As one PCP said: “We are measured according to how we perform and follow up on patients. We have high levels. This is important.” An administrator described: “They measure our performance, whether we follow up on patients, whether patients follow up on recommended tests. If [our clinic performs well compared to other clinics], then we are high on the chart. So as an encouragement, they give us a treat.”
Staff at low-TR clinics seemed to be less familiar with these incentives, as suggested by the following nurse: “I have not heard of incentives provided by the administration to follow-up on patients.”
DISCUSSION
Challenges faced by the health care staff to engage patients in regular, proactive patterns of primary care visits have been widely reported.36-38 Only a highly functional health care team can overcome these challenges to promote a more regular pattern of follow-up visits.39,40 We undertook this qualitative study to compare clinics with more– and less–temporally regular patterns of primary care visits and to learn what strategies clinics can adopt to promote more regular follow-up through more effective patient engagement. While most studies focus on nurse-physician relationships, the uniqueness of this study is that it included the perspectives of the administrative staff and pharmacists.
Our main findings suggest that high-TR clinics are characterized by close working relationships among staff. Corresponding with the Organizational Dimensions of the Structuration Model of Collaboration28,29 and Sullivan’s framework of collaboration,30 high-TR clinics show fewer hierarchical and more flat structures within the staff. The interviewees described flat relationships which allude to a more democratic team, where every team member is part of the decision-making process.41,42 They described an interdisciplinary team where team members align in their values and must depend on one another to complete the task of persuading patients to visit the PCP regularly and follow up with medical recommendations.43,44
Studies about teamwork in health care systems emphasize interdependency and shared goals.16,17,45 In addition to these elements, this study’s findings highlight role alignment, where PCPs perceived that their role aligned with the nurse and the administrative staff when motivating patients to follow up.
Further, effective teams improve patient safety by partnering with patients, adapting to their needs, and cultivating personal relationships.46-48 The high-TR staff in this study suggested implementing an adaptive workflow system, and constantly and informally communicating with patients. While these techniques might have improved follow-ups of challenging patients, they might also result in exhausting the staff.49 Interestingly, the high-TR staff described being motivated to pursue challenging patients and did not discuss the burden of off-work communication with patients, further underpinning the importance of working within effective interdisciplinary health care teams.
High-TR-clinics were characterized by 6 techniques and best practices to facilitate follow-ups of chronic patients. They emphasize the importance of having a system of follow-up. These strategies contributed to higher-functioning health care teams and would be worth emulating more widely by clinics looking to improve their performance. It would also be worth designing an interventional study to measure the impact of a formal attempt to promote these strategies on TR, as well control of chronic conditions.
Limitations
This study has limitations. We only compared the TR of clinics within the LHS system to each other. It may be that none of the clinics in our study is achieving what would be an ideal level of TR yet, but there is no way to know for sure. Also, we excluded patients’ perspectives at the participating clinics, which could provide additional insights regarding how some clinics achieve higher TR. Further, the study included a limited number of participants from each group, which limits the generalizability of our findings.
CONCLUSIONS
This study suggests that stronger teamwork between staff members and an interdisciplinary team where every team member is part of the process of promoting regular follow-ups of patients with chronic conditions can result in proactive medicine and improve patients’ regular follow-ups with medical recommendations in primary care settings. The 6 strategies mentioned by high-TR staff members that contribute to patients’ follow-up may be useful to educational and clinical programs promoting patient-centered care50,51;specifically, programs focusing on how medical staff utilize their dynamics and close relationships to improve health outcomes and how PCPs’ role alignment with the health care staff can facilitate regular follow-ups of challenging patients.
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest: authors report none.
Author contributions: Study design: M.K., A.J.R. Obtained funding: A.J.R. Analysis and interpretation: M.K., L.S., A.J.R. Drafted the manuscript: M.K. Revised the manuscript for important intellectual content: all authors. Approved the final manuscript: all authors. Study supervision: A.G-C., A.J.R.
Funding support: Funded by a grant from the Israel Science Foundation (Grant 764/21) to Dr Rose.
Ethics approval and consent to participate: All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. The study was approved by the Leumit Health Services (LHS) research ethics committee. Informed consent was waived by the Leumit Health Services research ethics committee.
Availability of data and materials: Leumit Health Services data can be made available to researchers who partner with an LHS researcher, and who apply for data access. The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
- Received for publication April 9, 2024.
- Revision received October 23, 2024.
- Accepted for publication October 30, 2024.
- © 2025 Annals of Family Medicine, Inc.