Article Figures & Data
Figures
Tables
1. On average, during the past week, how often were you woken by your asthma during the night? 0 Never 1 Hardly ever 2 A few times 3 Several times 4 Many times 5 A great many times 6 Unable to sleep because of asthma 2. On average, during the past week, how bad were your asthma symptoms when you woke up in the morning? 0 No symptoms 1 Very mild symptoms 2 Mild symptoms 3 Moderate symptoms 4 Quite severe symptoms 5 Severe symptoms 6 Very severe symptoms 3. In general, during the past week, how limited were you in your activities because of your asthma? 0 Not limited at all 1 Very slightly limited 2 Slightly limited 3 Moderately limited 4 Very limited 5 Extremely limited 6 Totally limited 4. In general, during the past week, how much shortness of breath did you experience because of your asthma? 0 None 1 A very little 2 A little 3 A moderate amount 4 Quite a lot 5 A great deal 6 A very great deal 5. In general, during the past week, how much of the time did you wheeze? 0 Never 1 Hardly any of the time 2 A little of the time 3 A moderate amount of the time 4 A lot of the time 5 Most of the time 6 All the time 6. On average, during the past week, how many puffs/inhalations of short-acting bronchodilator (eg, Ventolin, Bricanyl) have you used each day? (If you are not sure how to answer this question, please ask for help.) 0 None 1 1–2 puffs/inhalations most days 2 3–4 puffs/inhalations most days 3 5–8 puffs/inhalations most days 4 9–12 puffs/inhalations most days 5 13–16 puffs/inhalations most days 6 More than 16 puffs/inhalations most days - Table 2.
Characteristics of All Patients Sent the ACQ and of Respondents and Nonrespondents
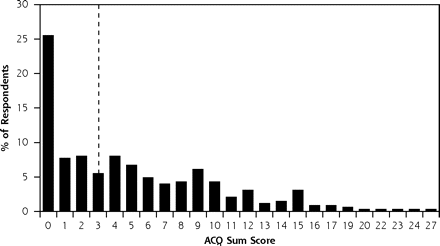
Group Characteristic Total (N = 434) Nonrespondents (n = 101) Respondents* (n = 333) P Value ACQ = Asthma Control Questionnaire.14,16 Note: Values are % (No.) unless indicated otherwise. * Primary and secondary respondents combined. † Calculated with the χ2 test. ‡ Calculated with the 1-way analysis of variance test. § Patients who visited their family physician for respiratory complaints, including visits for asthma exacerbations. || In the 2 years preceding the ACQ mailing. ¶ Calculated with the Mann-Whitney U test. # Receipt of at least 1 prescription for a bronchodilator or an inhaled steroid in the 2 years preceding the ACQ mailing. ** Proportion of inhaled steroid users; dosing groups are based on the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) classification.19 †† At least 1 exacerbation for which prednisolone or antibiotics were prescribed. Female 58.5 (254) 45.5 (46) 62.5 (208) .003† Age, mean (SD), years 34.1 (7.5) 32.6 (7.5) 34.6 (7.5) .02‡ Visitors§ 47.7 (207) 47.5 (48) 47.7 (159) .97† Consultations, || mean (SD), No. 1.1 (1.8) 1.0 (1.6) 1.2 (1.9) .45¶ Use of any asthma medication# 75.3 (327) 61.4 (62) 79.6 (265) <.001† Use of inhaled steroid 26.0 (113) 16.8 (17) 28.8 (96) .02† Low dose** 8.5 (37) 17.6 (3) 35.8 (34) – Intermediate dose** 9.4 (41) 29.5 (5) 37.9 (36) .08† High dose** 7.8 (34) 52.9 (9) 26.4 (25) – Short-acting bronchodilator 23.7 (103) 19.8 (20) 24.9 (83) .29† Long-acting β2 agonist 6.0 (26) 5.0 (5) 6.3 (21) .61† Asthma exacerbation†† 12.0 (52) 8.9 (9) 12.9 (43) .28† ACQ sum score, mean (SD) – – 5.2 (5.2) – Characteristic Primary Respondents (n=244) Secondary Respondents (n=89) P Value ACQ = Asthma Control Questionnaire.14,16 Note: Values are % (No.) unless indicated otherwise. * Calculated with χ2 test. † Calculated with 1-way analysis of variance test. ‡ Patients who visited their family physician for respiratory complaints, including visits for asthma exacerbations. § In the 2 years preceding ACQ mailing. Calculated with Mann-Whitney U test. ¶ At least 1 prescription for a bronchodilator or an inhaled steroid in the 2 years preceding the ACQ mailing. # At least 1 exacerbation for which prednisolone or antibiotics were prescribed. Female 65.2 (159) 55.1 (49) .09* Age, mean (SD), years 34.6 (7.3) 34.6 (8.1) .94† Visitors‡ 50.4 (123) 40.4 (36) .11* Consultations,§ mean (SD), No. 1.3 (2.1) 0.8 (1.2) .03|| Use of any asthma medication¶ 83.2 (203) 69.7 (62) .007* Asthma exacerbation# 13.9 (34) 10.1 (9) .46* ACQ sum score, mean (SD) 5.3 (5.3) 4.8 (5.2) .49||